pGina MySQL Authentication Plugin Documentation
- Plugin Name: MySQL Authentication
- Plugin Type: Authentication
- Latest Version: 3.0.0.0
How it Works
The MySQL Authentication plugin authenticates users against account information stored in a MySQL database. The plugin connects to the MySQL server, retrieves the account information including password (possibly a hash), and compares the user supplied password with the one retrieved from the database. It registers success if the passwords (or hashes) match.
The MySQL Authentication plugin expects user information to be stored in a table with a specific schema. The configuration UI can be used to create the table (see below). Users can be added using standard SQL. Since pGina does not currently support password changes, password changes currently need to be supported by your own tools.
Typical Setup
A typical (minimal) setup for MySQL Authentication is to enable the Local Machine plugin in the authentication and gateway stages, and enable MySQL Auth. in the authentication stage. Within the authentication stage, order the MySQL plugin before Local Machine.
The User Information Table
User information must be stored in the MySQL database within a table that has at least the following columns:
user- The user name. This column should be unique (or the primary key).hash_method- The hash method used for storing the password. This can be one of several strings (see below).password- The (possibly hashed) password.
The data type of the columns should be a string type such as TEXT or VARCHAR, but be careful of length limitations.
The hash_method column can have one of the following values:
NONE- The password is stored in plain text.MD5,SHA1,SHA256,SHA384, orSHA512SMD5,SSHA1,SSHA256,SSHA384, orSSHA512(The salted versions of above)
Salted Passwords
If any of the salted hash methods are used, this plugin expects the data to be organized as follows. The password column must contain a hexadecimal or base 64 encoded string that contains the following:
encoding ( hash( password + salt ) + salt )
Where encoding converts to a string using either hexadecimal or base 64 encoding, and hash applies the appropriate hash algorithm.
Configuration
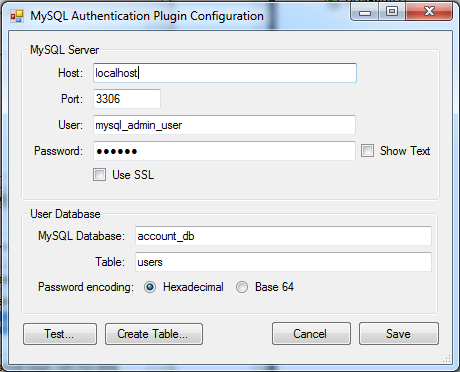
- Host – The IP or fully-qualified hostname of the MySQL server.
- Port – The port where the MySQL server process is listening.
- User – The username to use when connecting to the MySQL server.
- Password – The password to use when connecting to the MySQL server.
- Use SSL – Whether or not to use SSL encryption when connecting to the MySQL server. Note that for this to work correctly, your MySQL server must have SSL enabled. For more information on setting up a MySQL server with SSL, see the MySQL documentation.
- MySQL Database – The database containing the account information table.
- Table – The name of the account information table (see above).
- Password encoding – The binary encoding used in the
passwordcolumn of the database.
The “Test…” button initiates a test of the MySQL connection, and verifies that the account table exists and is properly formatted.
The “Create Table…” button attempts to connect to the MySQL server and create the account information table.
